Leak Detection Analysis
Posted on May 25, 2023 Big Data Machine Learning & AI
Detecting leaks in pipes is crucial for damage prevention and resource conservation. Traditional leak detection methods, which rely on visual or auditory cues may miss small leaks and in certain cases be unreliable. This is where negative pressure waves (NPW) and machine learning come into play.
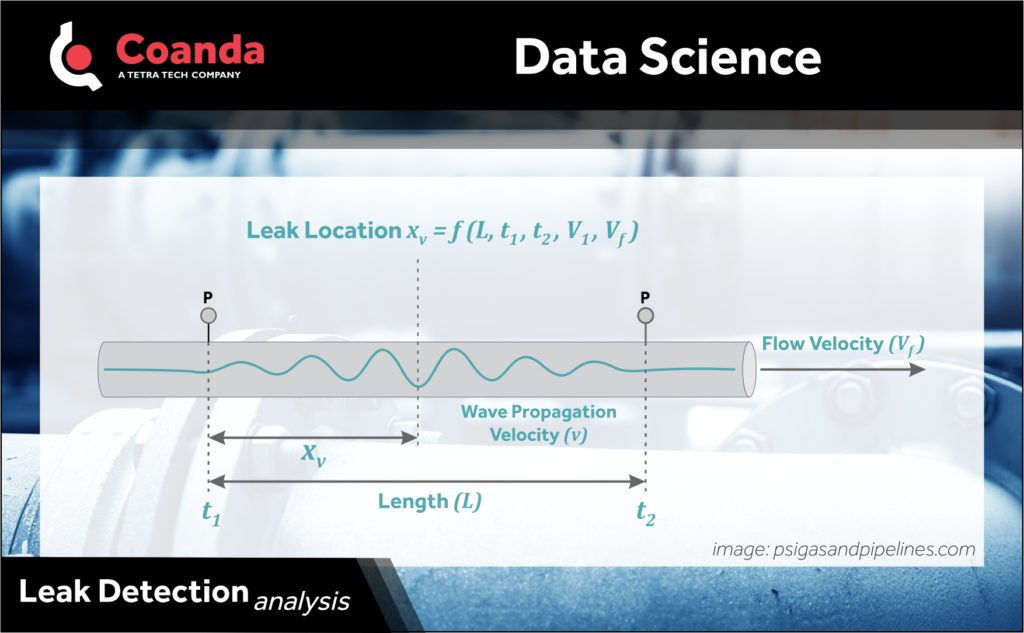
Analyzing pressure signals is the basis of NPW. In the event of a leak in a pipe, a negative pressure wave is generated, which travels both upstream and downstream. Various points of measurement experience a decrease in pressure as a result of this wave.
The negative pressure wave generated by a leak in a pipe not only indicates the presence of a leak (from the induced pressure drops at measurement points) but can also be used to locate the leak. The time difference of arrival (TDOA) of a negative pressure wave between upstream and downstream sensors can be used to calculate the distance traveled by the wave and locate the leak.
This method of using TDOA to locate leaks has several advantages. It is non-invasive, meaning that there is no need to dig up the pipe or otherwise disrupt its operation in order to detect the leak. It is also highly accurate, allowing for precise location of the leak, and can be performed efficiently.
Machine learning algorithms can then analyze the data from these sensors to identify patterns and anomalies that could indicate a leak. By training the algorithm on a large dataset of known behavior, it can learn to recognize the unique characteristics of a leak and distinguish it from other types of noise in the system.
Combining negative pressure wave technology with machine learning can greatly increase the accuracy and efficiency of leak detection in pipes. Not only does it reduce the likelihood of false alarms or missed leaks, but it also allows for early detection and intervention, preventing costly damage and waste.