Chemical & Process Engineering – Centrifuge Scaling
Posted on December 27, 2022 Process Engineering Separation
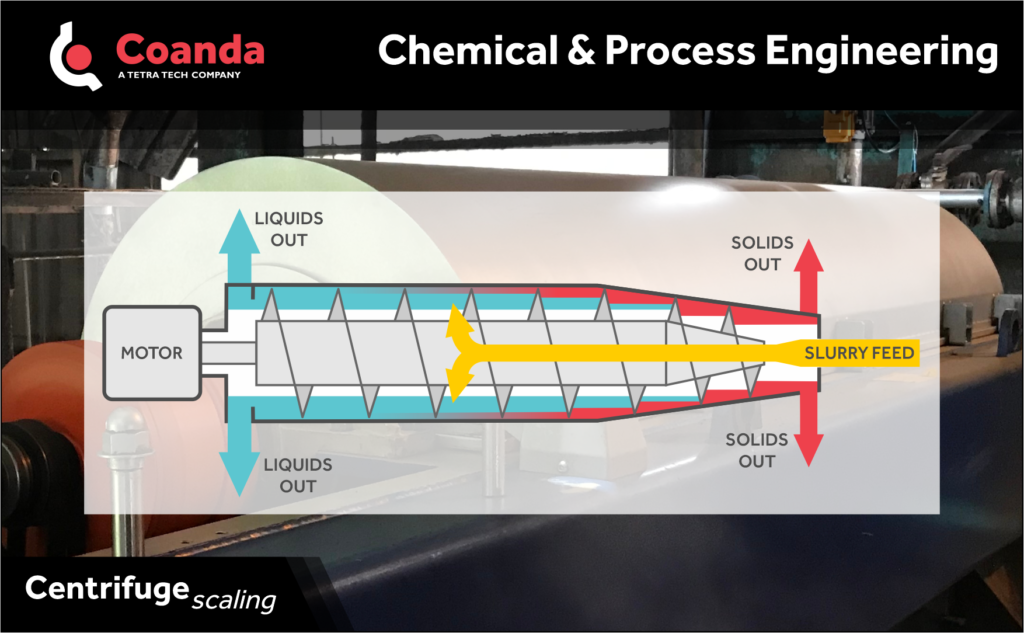
Centrifugation is used to separate materials by density – e.g., separating solids from liquids, or separating oil and water. As material spins in the rotating vessel, centrifugal force pushes the heavier components to edge of the vessel, away from the axis of rotation and light components move towards the axis of rotation. For continuous (as opposed to batch) centrifuges, discharge ports at various positions allow for collection of the different density fractions. Internal mechanisms, e.g., an auger in a decanter centrifuge or inclined surfaces in a disc stack centrifuge, can be used to aid in separation.
Industrial centrifuges can be complex and costly. Bench-scale tests are typically used to evaluate material separability prior to investment in large-scale centrifugation equipment. Various methods and rules of thumb have been developed to scale performance between bench-, pilot-, and plant-scale centrifuges. One method is known as the sigma parameter approach. The sigma parameter is the ratio between the feed rate of material into the centrifuge and the equivalent settling area. The equivalent settling area is the area of a gravitational settler that would be required to match the idealized performance of the centrifuge, which can be calculated based on the centrifuge type, size, and speed.
The sigma parameter approach offers a convenient, well-defined method for comparing centrifuge types, sizes, and operating parameters. However, there are significant assumptions behind this approach. Other considerations must typically be taken into account when scaling centrifugation processes. For example, material entering a centrifuge experiences large shear forces as it is accelerated to the rotational speed of the centrifuge. This can cause mechanical deformation or breakage of fragile components like cells or emulsified droplets, leading to undesirable product components or making the material more difficult to separate. This effect may not be seen in benchtop testing due to the scale and geometry of smaller centrifuges and is not reflected in the sigma parameter method.