Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Posted on March 11, 2021 Cleantech
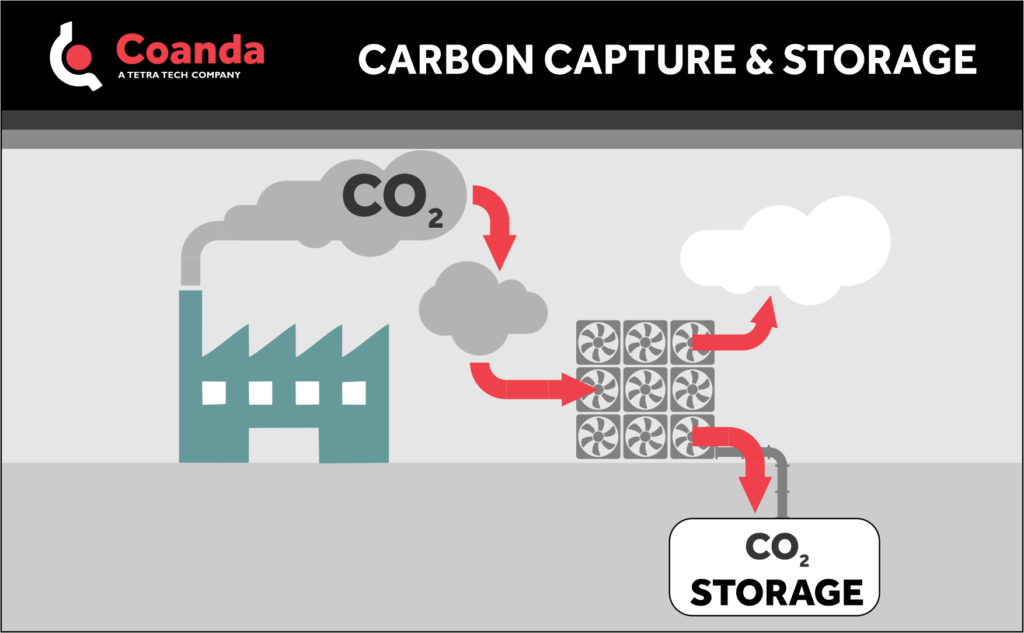
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) involves:
- ‘Capturing’ carbon dioxide (CO2) in as concentrated a form as possible
- Transporting the concentrated stream to the point of sequestering
- Depositing the CO2-laden stream into a storage site where it will not be allowed to re-enter the atmosphere
Carbon capture technologies generally target industrial waste streams, contacting them with liquids or solids that selectively remove CO2 from process gas.
Direct Air Capture (DAC) is a specific approach to carbon capture that removes CO2 directly from the air. Transport to the storage location typically occurs via pipeline, where the concentrated CO2 is often injected into deep geological formations that have the appropriate characteristics. Other approaches to storage involve forming carbonate salts or using the CO2 as a food source for algae.
Each step of the CCS process has its own set of unique technical challenges, covering a broad range of scientific disciplines, including thermodynamics, chemistry, geochemistry, fluid mechanics, reaction engineering, and mass transfer. Coanda’s multi disciplinary team has the experience necessary to successfully tackle these challenges head-on.
Get in touch to discuss your Carbon Capture issues today.


